Backup Power Supply for Oxygen Concentrators
When it comes to ensuring the health and well-being of individuals who rely on oxygen concentrators, one critical factor often goes overlooked: Backup Power Supply for Oxygen Concentrators. Oxygen concentrators are lifelines for those with respiratory conditions, providing a continuous supply of oxygen to help them breathe comfortably.
However, power outages and interruptions can pose a serious risk to patients who depend on these devices. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the importance of a backup power supply for oxygen concentrators, exploring the types of backup power options available, how to choose the right one and tips for maintaining a reliable backup system.
Understanding Oxygen Concentrators
To fully grasp the significance of backup power in the context of oxygen concentrators, it's essential to begin by gaining a comprehensive understanding of what these devices are and how they function.
What Is an Oxygen Concentrator?
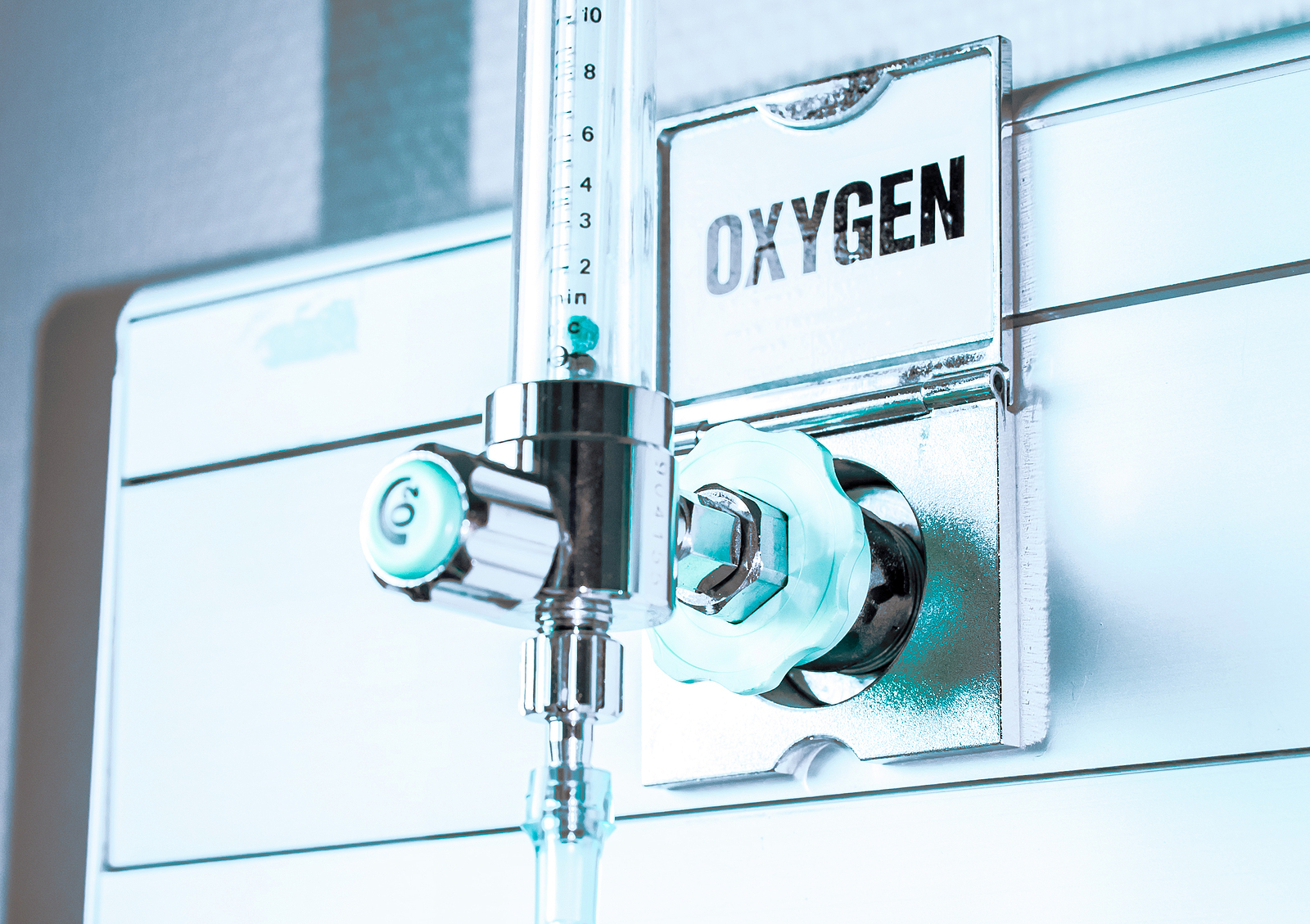
An oxygen concentrator stands as a vital medical apparatus designed to offer a continuous supply of oxygen to individuals grappling with respiratory ailments like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, or sleep apnea.
In stark contrast to traditional oxygen tanks, which necessitate periodic refilling, oxygen concentrators employ a unique mechanism to extract oxygen from the surrounding atmosphere, rendering them a more user-friendly and cost-efficient solution.
How Do Oxygen Concentrators Work?
The operation of oxygen concentrators unfolds as follows: they draw ambient air into their systems and guide it through a meticulous series of filters, adept at stripping away nitrogen molecules. This meticulous process leaves behind a potent concentration of oxygen.
Subsequently, the purified oxygen is meticulously channeled to the patient via either a nasal cannula or an oxygen mask. This delivery method allows patients to breathe more comfortably and maintain optimal oxygen levels in their bloodstream, offering them a lifeline in managing their respiratory conditions.

The Importance of Backup Power Supply for Oxygen Concentrators
Power outages are an unpredictable occurrence that can have grave implications, particularly for individuals dependent on oxygen concentrators. The absence of a Backup Power Supply for Oxygen Concentrators can expose patients to sudden interruptions in their vital oxygen therapy, resulting in potentially life-threatening consequences such as hypoxia (oxygen deficiency).
Power outages can lead to a cascade of detrimental effects for patients relying on oxygen concentrators powered by the main electrical grid:
- Decreased Oxygen Levels: When the power goes out, oxygen concentrators cease functioning, causing a rapid decline in oxygen levels in the patient's bloodstream. This results in oxygen desaturation, increased breathlessness, and an immediate threat to the patient's well-being.
- Risk of Hospitalization: Inadequate oxygen supply during a power outage may necessitate emergency medical interventions or hospitalization, placing further stress on patients and healthcare resources.
- Emotional Impact: Power outages not only jeopardize physical health but also induce anxiety and stress in both patients and their caregivers. The uncertainty and fear of not having access to life-saving oxygen therapy can exacerbate an already challenging situation.
- Compromised Quality of Life: For individuals who rely on oxygen therapy to maintain their daily activities and overall quality of life, power outages can disrupt their routines and independence, leading to a compromised quality of life.
Types of Backup Power Options
Maintaining an uninterrupted oxygen supply is paramount for individuals reliant on oxygen concentrators. To achieve this, a range of backup power options exists, each catering to specific needs, equipment types, and budget considerations. Here, we delve into the various alternatives to empower you with the knowledge needed to make an informed choice.
Battery-Powered Oxygen Concentrators:
Battery-powered oxygen concentrators are designed for autonomy from main power sources. These units feature rechargeable batteries, enabling the continuation of oxygen therapy during power outages. Consider the following factors when selecting a battery-powered concentrator:
- Battery Life: Different models offer varying battery life spans, so assess your requirements and choose accordingly.
- Charging Options: Understand the duration required for a full battery recharge and inquire about the availability of additional batteries for extended use.
- Portability: Battery-powered concentrators are often lightweight and portable, making them ideal for those who need to travel or move around during therapy.
Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS):
While typically associated with computers and electronics, a UPS can also be repurposed to safeguard oxygen concentrators against power interruptions. When considering a UPS, keep the following aspects in mind:
- Capacity: Ensure that the UPS can handle the power demands of your specific oxygen concentrator model.
- Backup Time: UPS devices come in various sizes, offering diverse backup durations. Select one that aligns with your expected needs.
- Maintenance: Regularly monitor and replace UPS batteries as required to maintain reliability during critical moments.
Backup Generators:
Backup generators offer a robust and comprehensive solution to ensure continuous power for oxygen concentrators, whether for individual use or powering an entire household. Consider these factors when evaluating backup generators:
- Generator Type: Choose between portable generators, standby generators, and inverter generators, each suited to different requirements and situations.
- Fuel Source: Assess the availability and convenience of the chosen fuel source, which can be gasoline, propane, or natural gas, to power your generator.
- Installation: Recognize that standby generators necessitate professional installation, while portable generators provide more flexibility and ease of use.

Choosing the Right Backup Power Solution
Ensuring uninterrupted access to your oxygen concentrator is vital, and choosing the appropriate backup power solution involves several critical considerations. To make an informed decision, take into account the following factors:
Device Compatibility
Start by verifying that the backup power source you select is fully compatible with your specific oxygen concentrator model. Consult the manufacturer's guidelines or contact their customer support for any necessary clarifications. It's crucial to ensure that the backup power solution can safely and effectively power your concentrator.
Runtime Requirements
Analyze your daily usage patterns and take into consideration the typical duration of power outages in your region. This information will help you determine the required runtime for your backup power solution. It's essential to select a backup option that can provide sufficient power for an extended period to meet your needs comfortably during emergencies.
Portability and Convenience
Evaluate the ease of transporting and setting up your chosen backup power solution. If you intend to use your oxygen concentrator while on the move or during outdoor activities, consider highly portable options such as battery-powered concentrators. On the other hand, backup generators may require more effort to set up and may not be as convenient for mobile use.
Budget
Understand that different backup power solutions come with varying price tags. Assess your budget carefully and weigh it against the reliability and safety of the options available. While it's tempting to opt for the cheapest solution, prioritize a backup power source that ensures the uninterrupted functioning of your oxygen concentrator, especially if it is a life-critical medical device.
Maintaining Your Backup Power System
Ensuring a consistent and dependable backup power supply for your oxygen concentrator is of utmost importance. To achieve this, it is vital to perform regular maintenance and adhere to recommended best practices to keep your backup power system in optimal condition.
Battery Maintenance
If your oxygen concentrator relies on battery-powered devices or uninterruptible power supply (UPS) units, consider the following maintenance guidelines:
- Regular Battery Charging: Make it a habit to charge the batteries of your concentrator or UPS units on a routine basis. Keeping batteries adequately charged ensures they are ready to provide power when needed most.
- Battery Replacement: Keep a vigilant eye on your batteries' performance. When you notice that they no longer hold a charge effectively or exhibit signs of deterioration, promptly replace them. This proactive approach will help prevent unexpected power interruptions.
- Storage Conditions: Store spare batteries in a cool and dry environment. Maintaining a suitable storage environment can extend the lifespan of your backup batteries and ensure they are always available as backup power sources.
Generator Maintenance
For individuals relying on backup generators as their primary power source during outages, thorough and regular maintenance is essential. Follow these maintenance recommendations:
- Scheduled Inspections and Servicing: Arrange routine inspections and servicing of your backup generator by a qualified technician. These professionals can identify and address any issues that may compromise the generator's functionality.
- Periodic Testing: Test your generator periodically to verify that it starts and operates correctly. Regular testing ensures that the generator is in working order when you need it most, reducing the risk of power disruptions.
- Fuel Supply Management: Maintain an ample supply of fuel for your generator and establish a rotation system to ensure the fuel remains fresh and reliable. Having an adequate fuel reserve is critical for sustained operation during extended power outages.
Legal and Safety Considerations
When implementing backup power solutions, it's essential to take into account a range of legal and safety considerations to ensure both compliance and the well-being of individuals. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
Local Regulations and Zoning Laws
Before installing backup generators, it's imperative to thoroughly research and understand local regulations and zoning laws. Different regions may have specific requirements and restrictions regarding the installation, operation, and placement of backup power sources. Compliance with these regulations is crucial to avoid legal issues and potential fines.
Carbon Monoxide (CO) Safety
Safety should always be a top priority when using backup generators. To prevent carbon monoxide poisoning, ensure proper ventilation in the area where the generator is located. CO is a colorless and odorless gas that can be lethal when inhaled in high concentrations. Adequate ventilation can help dissipate CO emissions, safeguarding the health and lives of those nearby.
Noise Regulations
Noise pollution can be a significant concern, especially in residential neighborhoods. Many areas have noise regulations in place to maintain a peaceful environment for residents. When operating backup generators, be aware of any noise restrictions that may apply in your locality. Some regions may have specific hours during which generator use is permitted, or they may impose decibel limits. Complying with noise regulations not only ensures the comfort of your neighbors but also helps avoid potential legal disputes.
Emission Regulations
Depending on your location and the type of backup power source you choose, there may be emissions regulations to consider. Diesel generators, for example, can produce emissions that contribute to air pollution. Research the emissions standards applicable to your area and select a generator that meets or exceeds these requirements. Additionally, some regions may require permits for the installation and operation of generators emitting pollutants.
Electrical Codes and Standards
Ensure that your backup power system complies with local electrical codes and standards. These codes dictate proper wiring, grounding, and electrical connections to prevent electrical hazards and fires. Non-compliance can result in unsafe conditions and may void insurance coverage.
Fuel Storage and Handling
If your backup power source relies on fuels such as diesel, propane, or natural gas, you'll need to adhere to regulations governing fuel storage and handling. Proper storage tanks, safety measures, and containment systems are often required to minimize the risk of leaks, spills, and fire hazards.
Emergency Preparedness Plan
Establishing a comprehensive emergency preparedness plan is of paramount importance to safeguard yourself and your loved ones during unforeseen crises. Here are several key components to consider when creating an effective emergency preparedness plan:
Evacuation Plan
Develop a well-thought-out evacuation plan that covers various scenarios, including extended power outages, natural disasters, or other emergencies. Identify safe locations where you can seek refuge, whether it's a designated emergency shelter, the home of a trusted friend or family member, or a secure community center. Make sure everyone in your household is familiar with the plan and knows the escape routes.
Communication Strategy
Establish a reliable communication strategy to stay connected with family, friends, and essential medical professionals during emergencies. This may involve setting up a communication tree or using mobile apps, walkie-talkies, or satellite phones. Ensure that all family members have contact information for each other and know where to meet if separated.
Emergency Kit
Assemble a comprehensive emergency kit containing essential supplies tailored to your specific needs. This kit should include, but is not limited to:
- Medications and medical supplies: Stock an ample supply of necessary medications, medical equipment, and any lifesaving devices. For individuals requiring oxygen therapy, have extra oxygen tanks and tubing readily available.
- Backup power sources: Include backup batteries for medical devices, such as oxygen concentrators or CPAP machines. Make sure they are charged and functional.
- Non-perishable food and water: Store a sufficient quantity of non-perishable food items and clean drinking water to sustain your household for at least several days.
- First aid supplies: Include a well-equipped first aid kit with bandages, antiseptics, prescription medications, and any specific medical supplies required for your family's health conditions.
- Flashlights, lanterns, and batteries: Ensure you have a reliable source of illumination in case of power outages. Store extra batteries to keep these devices functioning.
- Personal hygiene items: Pack toiletries, sanitation supplies, and hygiene products to maintain cleanliness and comfort.
- Important documents: Keep copies of essential documents such as identification, insurance policies, medical records, and contact information in a waterproof container.
- Cash and cards: Have a reserve of cash in small denominations and credit/debit cards for emergencies.
Special Considerations
If you or someone in your household has specific medical needs or mobility limitations, take these into account when creating your emergency plan. Consider arrangements for accessible transportation, additional medical supplies, and accessible shelter options.
Regular Review and Update
Periodically review and update your emergency preparedness plan and kit to ensure they remain relevant and effective. Replace expired supplies, update contact information, and practice evacuation drills with your family to ensure everyone knows their roles and responsibilities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Backup Power Supply for Oxygen Concentrators
Q1: Do oxygen concentrators have a backup battery?
A1: Oxygen concentrators typically do not come with built-in backup batteries. They rely on a continuous power source to function. However, some portable oxygen concentrators may have optional external battery packs that can provide extended usage when no power source is available. It's essential to check the specific model's features to determine if a backup battery option is available.
Q2: What is the backup system for oxygen medical device power?
A2: The backup system for oxygen concentrators often involves having alternative power sources available in case of a power outage. This can include having backup oxygen tanks or cylinders filled and ready for use when electrical power is unavailable. It's important for individuals relying on oxygen concentrators to have a backup plan in case of power disruptions.
Q3: How many watts are needed to power an oxygen concentrator?
A3: The power requirements for oxygen concentrators can vary depending on the specific make and model. Generally, most home-based oxygen concentrators consume around 300 to 600 watts of electricity. Portable oxygen concentrators may have lower power requirements. It's essential to check the user manual or consult with the manufacturer to determine the exact wattage needed for your particular oxygen concentrator.
Q4: What size power inverter do I need to run an oxygen concentrator?
A4: If you intend to use an oxygen concentrator with a power inverter in a vehicle or during power outages, you should choose an inverter that can handle the wattage requirements of your concentrator. As mentioned earlier, concentrators typically require 300 to 600 watts. Therefore, you should select a power inverter with a continuous output rating greater than the maximum wattage of your concentrator. It's also important to consider the inverter's input voltage compatibility and safety features.
Q5: Can an oxygen concentrator run on a UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply)?
A5: Yes, oxygen concentrators can be connected to a UPS to provide temporary backup power during short power outages. However, the UPS must have a sufficient capacity (in terms of both wattage and battery runtime) to support the oxygen concentrator's power requirements. It's crucial to ensure that the UPS can maintain power long enough to prevent interruptions in oxygen therapy.
Q6: Can an oxygen concentrator run without electricity?
A6: Oxygen concentrators are primarily designed to operate using electricity. They rely on power to extract oxygen from the surrounding air. However, as mentioned earlier, some portable models may offer the option of external battery packs for short-term use when electricity is not available. In emergency situations or extended power outages, individuals should have backup oxygen tanks or cylinders filled with oxygen to ensure a continuous oxygen supply when the concentrator cannot operate due to a lack of electricity. Always consult with a healthcare professional or the manufacturer for guidance on using Backup Power Supply for Oxygen Concentrators in various situations.
Backup Power Supply for Oxygen Concentrators Conclusion
A backup power supply for oxygen concentrators is not just a convenience but a critical necessity for individuals with respiratory conditions. Power outages can happen at any time, and having a reliable backup system in place can mean the difference between comfort and crisis. Whether you opt for battery-powered concentrators, UPS devices, or backup generators, the key is to choose a solution that aligns with your specific needs and to maintain it diligently.
Sources Studies for Backup Power Supply for Oxygen Concentrators
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6876135/
https://bmchealthservres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12913-019-4129-7
continue reading
Related Posts
Uninterruptible Power Supply APC In today's fast-paced digital world, maintaining […]
Uninterruptible Power Supply Energy Storage Uninterruptible Power Supply Energy Storage […]
Uninterrupted Power Supply for Sale In today’s digital age, where […]